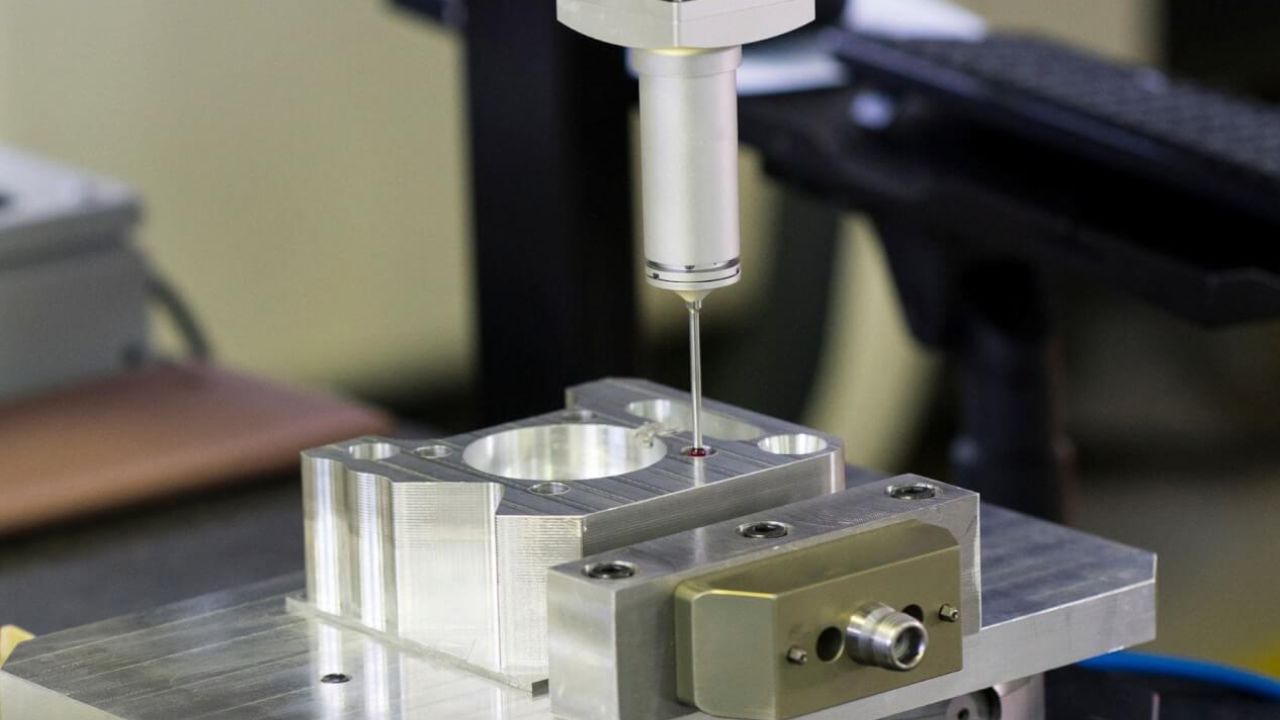
A crucial component of guaranteeing accuracy, consistency, and dependability in the manufacturing of parts and components in CNC machine shops is quality control. At these state-of-the-art manufacturing facilities, quality control procedures are carried out at different phases of the production process using computer numerical control (CNC) equipment that functions with remarkable accuracy.
Expert technicians and engineers closely monitor each stage, from material inspection and machine setup to machining operations and final product assessment. Newer CNC machines have built-in measurement systems that allow for real-time monitoring and adjustments, ensuring tolerances and dimensions are met.
Furthermore, comprehensive inspection utilizing specialized tools and equipment to evaluate elements like dimensional correctness, surface finish, and material integrity is part of quality control in cnc machine guide. Customers receive high-quality components for their applications thanks to these strict quality control procedures, which ensure that the produced parts fulfill all necessary norms and specifications.
Quality Control in CNC Machine Shops
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machine shops are the furnaces in which complex designs are turned into accurate parts. In these specialized workshops, quality control is a dedication to perfection rather than merely a procedure. The methods, equipment, and best practices used to attain unmatched accuracy and consistency are all covered in detail in this extensive guide, which dives into the complexities of quality control in CNC machine shops.
Pre-Production Planning
Long before the first tool comes into contact with the material, quality control is initiated. Carefully reviewing design parameters, material needs, and machining procedures is all part of pre-production planning. To ensure that the design is feasible to manufacture and that the chosen materials and toolpaths produce the intended results, engineers and machinists work together to identify possible obstacles.
Material Inspection
The final product’s quality greatly depends on the raw material’s integrity. Sophisticated instruments such as hardness testers and spectrometers make sure the material satisfies the requirements. By quickly addressing any deviations, the risk of defects is reduced and the machining process is started with a strong foundation.
Precision Machining
Precision cannot be compromised during the machining process. CNC devices are designed to carry out complex toolpaths with precision down to the micron. Expert machinists keep an eye on the procedure, making sure that the feeds, cutting speeds, and tool changes are tailored to the specific material. Multi-axis CNC machines allow for the production of intricate details and complex shapes, making complex operations possible.
In-Process Inspection
The in-process inspection entails watching the machining operation in real time. CNC machines incorporate sensors and measurement equipment to obtain information on temperature, cutting forces, and tool wear. Machinists can make quick adjustments thanks to this real-time input, which guarantees that the machining parameters stay within the predetermined tolerances.
Post-Machining Inspection
The finished components go through a thorough post-machining inspection after the machining process. Precision tools such as micrometers, calipers, and coordinate measuring machines (CMMs) are used in dimensional tests to verify critical dimensions and tolerances. Analysis of the surface finish verifies that the parts adhere to the required levels of roughness.
Quality Documentation
One of the main characteristics of quality control in CNC machine shops is extensive documentation. Every production run is well recorded, including material traceability, inspection findings, and specifications. In addition to being a source of reference for upcoming production runs, this paperwork also acts as traceability in the event of recalls and holds parties accountable for deviations.
Root Cause Analysis
CNC machine shops carry out root-cause analysis in the event of deviations or faults to determine the underlying problems. This entails a methodical examination of the elements that contributed to the issue, such as defects in the design, problems with the materials, or variations in the process. Root cause analysis offers insightful commentary that makes it possible to put remedial measures into place to stop reoccurring problems.
Client Collaboration
A key component of quality control is efficient client communication. CNC machine shops work closely with customers to comprehend their unique needs, tolerances, and performance standards. Frequent communication guarantees that any adjustments or alterations to the design are handled right away. Customer feedback is very important since it helps the shop match its procedures to the needs and vision of the client, which in turn improves customer pleasure.
Sum Up
It takes skill, accuracy, and dedication to perfection to carry out the complex process of quality control in CNC machine shops. CNC machine shops maintain the confidence of their customers and provide precision that exceeds expectations through strict standards and an ongoing improvement culture. In a world where accuracy is critical, quality control in CNC machining is a monument to human ingenuity, reshaping industries and propelling innovation with unflinching accuracy and uncompromising quality.